2022. 1. 10. 00:01ㆍNLP
저번 포스트에서는 논문 Efficient Estimation Of Word Representations In Vector Space를 소개하고 Word2Vec의 아키테쳐에 대해 설명했습니다. 이번에는 Word2Vec 중 Skip-gram 모델을 구현해보겠습니다.

Skip-gram은 Word2vec에서 제시한 모델 중 하나입니다. CBOW와 반대로 중심단어로 부터 주변단어를 예측합니다. 그림에서 볼 수 있듯이 Skip-gram의 모델의 imput layer는 하나이고 output layers는 주변단어의 수만큼 존재합니다. 따라서 각 output layer에서는 softmax with loss layer 등을 이용해 손실을 구하고 이 손실을 모두 더한 값이 최종 손실이 됩니다.
주변단어 수 만큼 손실을 계산해야하기 때문에 CBOW보다 학습 속도가 느리지만 단어분산표현의 정밀도 면에서 Skip-gram의 모델의 결과가 더 좋은 경우가 많습니다.
PyTorch를 사용하여 Skip-gram 알고리즘을 구현하는 과정입니다. kaggle의 text8.txt 데이터의 일부(1000개의 단어)로 학습했습니다. 중심단어를 입력했을 때, 그 주변단어를 도출될 확률을 높이도록 학습하는 것이 목표입니다.
import sys
sys.path.append('..')
from common.trainer import Trainer
from common.optimizer import Adam
from simple_cbow import SimpleCBOW
from common.util import preprocess, create_contexts_target, convert_one_hot
1. SkipGram 클래스
class SimpleSkipGram:
def __init__(self, vocab_size, hidden_size):
V, H = vocab_size, hidden_size
# 가중치 초기화
W_in = 0.01 * np.random.randn(V, H).astype('f')
W_out = 0.01 * np.random.randn(H, V).astype('f')
# 계층 생성
self.in_layer = MatMul(W_in) # 입력층
self.out_layer = MatMul(W_out) # 출력층
self.loss_layer1 = SoftmaxWithLoss() # Softmax 계층
self.loss_layer2 = SoftmaxWithLoss() # Softmax 계층
# 모든 가중치와 기울기를 리스트에 모은다.
layers = [self.in_layer, self.out_layer]
self.params, self.grads = [], []
for layer in layers:
self.params += layer.params
self.grads += layer.grads
# 인스턴스 변수에 단어의 분산 표현을 저장한다.
self.word_vecs = W_in- SimpleSkipGram 클래스의 인수
vocab_size : 어휘 수
hidden_size : hidden layer의 뉴런 수
- W_in , W_out 두개의 가중치
각각 작은 무작위 값으로 초기화 됩니다.
- 계층 생성
입력층의 Matmul 계층 1개
출력층의 Matmul 계층 1개
Softmax with Loss 계층 주변단어 수(=윈도우 크기) 만큼 (여기서는 2개)
2. 순전파 forward
def forward(self, contexts, target):
h = self.in_layer.forward(target)
s = self.out_layer.forward(h)
l1 = self.loss_layer1.forward(s, contexts[:, 0])
l2 = self.loss_layer2.forward(s, contexts[:, 1])
loss = l1 + l2
return loss3. 역전파 backward
def backward(self, dout=1):
dl1 = self.loss_layer1.backward(dout)
dl2 = self.loss_layer2.backward(dout)
ds = dl1 + dl2
dh = self.out_layer.backward(ds)
self.in_layer.backward(dh)
return None
4. 학습
## 학습데이터 준비과정
window_size = 1
hidden_size = 5 # 은닉층의 뉴런수
batch_size = 3
max_epoch = 1000
text = x # 데이터
corpus, word_to_id, id_to_word = preprocess(text) # corpus를 단어 id로 반환
vocab_size = len(word_to_id) # 어휘 수
contexts, target = create_contexts_target(corpus, window_size) # 중심, 주변단어 반환
# one-hot encoding
target = convert_one_hot(target, vocab_size)
contexts = convert_one_hot(contexts, vocab_size)## 모델학습
model_2 = SimpleSkipGram(vocab_size, hidden_size)
optimizer = Adam()
trainer_2 = Trainer(model_2, optimizer)
trainer_2.fit(contexts, target, max_epoch, batch_size)- 매개변수 갱신 방법
Adam
5. 결과
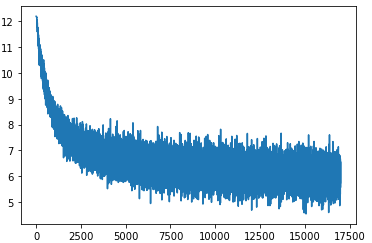
학습경과를 그래프로 나타내면 학습을 할 수록 손실이 감소하고 있는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
각 단어의 분산 표현은 다음과 같습니다.
ghosts [ -1.554753 -14.199934 5.4088864 -8.995648 -4.0544376]
mind [ 10.231861 -12.334701 2.9066288 2.9563556 5.0717473]
saying [ 0.6028301 -16.115307 0.48380145 -6.917041 2.6495762 ]
reality [ 14.173826 -0.3625413 -10.682704 4.753849 8.219211 ]
advocated [13.001251 3.5767713 -6.613554 9.323543 7.023613 ]
# (중략)단어를 벡터화시키는 것이 가능해졌습니다. 즉 분산표현으로 단어의 의미를 나타냈습니다.
reference
Word2Vec ⌜Efficient Estimation Of Word Representations In Vector Space⌟
밑바닥부터 시작하는 딥러닝2 (사이토 고키)
https://github.com/WegraLee/deep-learning-from-scratch-2/tree/master/ch03
https://www.kaggle.com/ashukr/implementation-of-word2vec-paper/data
'NLP' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Fasttext 논문 리뷰 : Enriching Word Vectors with Subword Information (0) | 2022.01.22 |
|---|---|
| GloVe 논문 리뷰 : Global Vectors forWord Representation (0) | 2022.01.16 |
| CBOW 코드 구현 : Word2Vec의 CBOW 모델 구현 (0) | 2022.01.07 |
| Word2Vec 논문 리뷰 : Efficient Estimation Of Word Representations In Vector Space (0) | 2022.01.03 |
| 토픽모델링: LDA(Latent Dirichlet Allocation) (0) | 2021.08.18 |